by
Muhammet Umut Danış | Jul 11, 2024
The list of academic projects at ITU - Faculty of Mechanical Engineering can be found in the details for a period of January and July 2024. We congratulate our researchers.
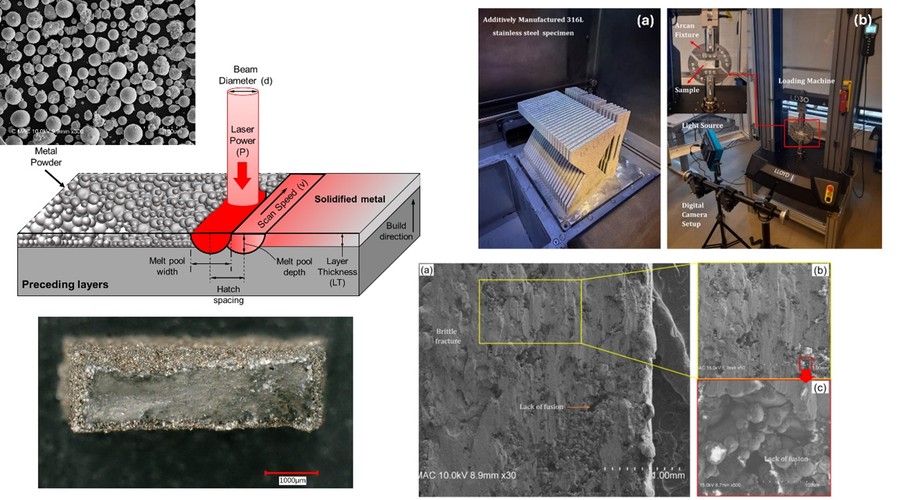
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF DAMAGE EVOLUTION IN THE ADDITIVELY MANUFACTURED METALLIC MATERIALS UNDER STATIC AND DYNAMIC LOADS
- Project Coordinator: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Rasid Ahmed Yildiz
- Organization Supporting the Project: ITU – BAP
Abstract:
The increasing demand for additively manufactured (AM) metal components in the industry raises questions regarding the mechanisms of damage formation in these materials. Therefore, this research proposal aims to experimentally investigate and numerically model the damage formation mechanisms in AM metal parts. The alloys SS316L, Inconel 625, and Ti-6Al-4V, produced using the laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) technique, will be utilized as the production method and materials for the samples in this study. The impact of additive manufacturing parameters on mechanical properties and fatigue behavior will be examined experimentally. The project plans to conduct porosity measurements, determine the melt pool geometry, perform hardness tests, assess surface topography, and carry out tensile and fatigue tests, as well as analyze fracture (damage) surfaces. Due to the inherent porosity of AM metal parts, modeling will be performed using the Gurson-Tvergaard-Needleman (GTN) damage model, a porous metal plasticity approach. To observe the micromechanical effects of deformation and loading conditions on the material structure, the surfaces of the parts subjected to all tests will be examined using SEM and the fracture surfaces will be analyzed. The experimentally obtained damage model parameters will be input into Abaqus finite element software, and the damage model will be defined. Considering the material's production parameters and mechanical behavior, strain path dependency and the effect of stress triaxiality will be investigated both experimentally and numerically. Following the experiments conducted under static conditions, the forged and AM parts will undergo dynamic (fatigue) tests, revealing the fatigue properties and behaviors of AM parts and distinguishing them from those of parts manufactured using traditional methods. At this stage, extensive imaging with SEM will be performed to analyze fracture and fatigue from a micromechanical perspective.
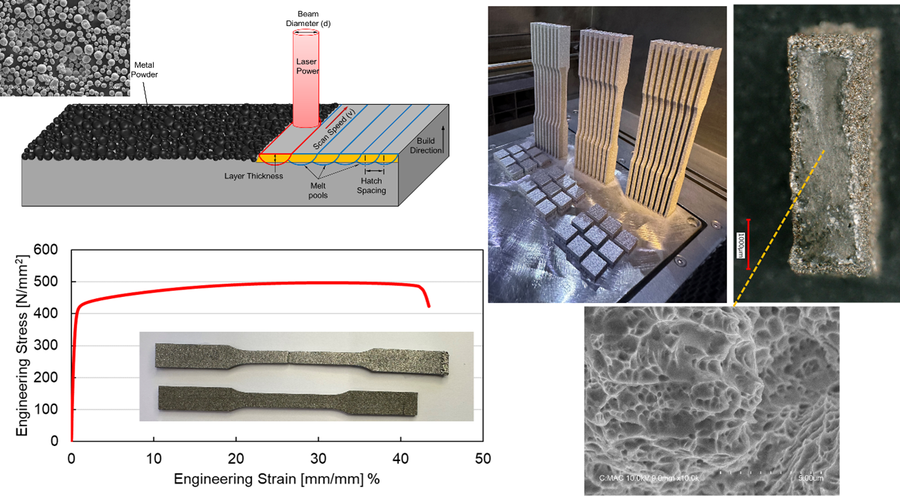
FAILURE ANALYSIS OF ADDITIVELY MANUFACTURED METAL PARTS
- Project Coordinator: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Rasid Ahmed Yildiz
- Organization Supporting the Project: Fabrikant Mads Clausens Fond
Abstract:
The European Union (EU) has long been a global hub for automotive industry and mechanical engineering, with an established reputation for producing high-quality heat exchangers, brakes, and clutches. Given the European Union's commitment to environmental regulations and reducing the carbon footprint of products, it is imperative for manufacturing and mechanical design engineers to be proficient in sustainable design, production, and supply chain practices. Within the framework of this project, failure analysis of additively manufactured parts, particularly those used in heat exchangers and the automotive sector, will be conducted. Research will be carried out on the failure analysis of additively manufactured parts under static and dynamic loading conditions. Moreover, by equipping the next generation of engineers with advanced failure analysis skills, the project aims to reduce product failure rates, enhance safety, and improve the overall reliability of heat exchangers and automotive parts. Additionally, this study will highlight the importance of sustainability in product management for additively manufactured parts. The project will not only address technical aspects but also instill a sense of environmental responsibility in future engineers educated at SDU Sonderborg. Furthermore, the behavior of brittle or ductile fracture under various loading conditions such as static uniaxial tensile, biaxial tensile, compression, and dynamic loading will be examined in detail.